Field of Research
Microeconomic theory
Research Topics
Mechanism design, Game theory
Overview of Research
My research is about microeconomic theory, in particular, about the theory of design of economic institutions (often called “mechanism design”). It is overlapped with the field of “market design” or “information design”, and related to contract theory and game theory in many respects.
One of the most fundamental questions in microeconomic theory is “among many heterogeneous economic entities, who should be allocated what?” This big question comprises many smaller questions, including the following: “(Assuming some allocations are set as desirable) how should we implement it?” For example, imagine that a school has decided to help talented but economically struggling students with financial aid, as the desirable allocation of some of the school’s financial resources. In its implementation, however, it is not necessarily easy to identify which students precisely belong to that category. Studying what the optimal rule should be (in this case, in selecting the students) is the subject of study of the mechanism design theory.
As theoretical research, my goal is to extract the essence of many different kinds of economic design problems, to formulate it as a mathematical model and problem, and then to give feedback to actual problems by providing the key “insights” in those problems; rather than studying each individual real case in depth. In this sense, what we learn may not be directly useful in real life (sometimes frustrating indeed!). Nevertheless, I believe that this way of studying economic institution design, namely, “extracting the essence, mathematically analyzing it, and giving back feedback” would work as an important complement to the other (perhaps more directly practically relevant) ways of studying economic institutions. I hope that the students taking my courses have this viewpoint in their mind.
As a part of my recent research, let me briefly explain the project studying information disclosure between two economic agents in a long-term relationship. For example, imagine a team of a leader and a subordinate in a firm. The leader periodically obtains some news about the potential of their project (e.g., developing a new product). If it is good news, the leader can enhance the subordinate’s effort by disclosing this information; while if it is bad news, the subordinate would lose his incentive to work hard. What is the optimal information disclosure policy for the leader? “Fully disclosing if it is good news, while keeping silence if bad” is not necessarily the best policy, as the subordinate would realize that silence just means bad news.
By the way, this topic is about communication policies among individuals, rather than about economic institutions. In fact, both are the targets of my research (and that of the mechanism design theory), in the sense that both are about optimal policies taking into account other economic agents’ incentives. It is an interesting aspect of theoretical research that many seemingly distinct problems could be analyzed by the same approach.
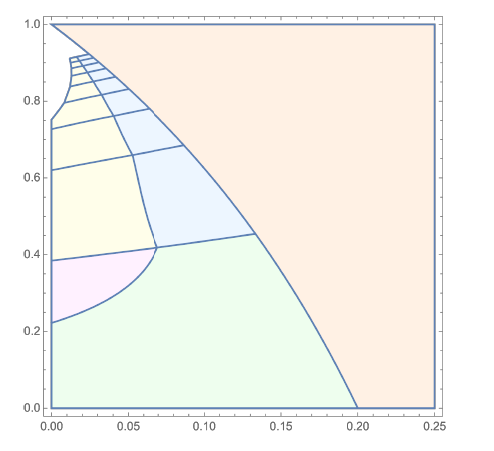
The figure summarizes the optimal disclosure policy. Very roughly, the left side of the figure corresponds to the cases where the leader’s news exhibits high time-wise correlation (e.g., if the news is bad today, it is likely to be bad tomorrow too); while the right side corresponds to the cases without much correlation. Let me ignore the vertical axis for now, and focus on the middle-height zone. The right-side of this zone (orange) is where it is optimal for the leader to fully disclose any information (both good and bad). This is a region where, even if the news is bad today, it is likely be good again tomorrow, and hence, there is not much rationale to hide the information. By being transparent, the leader can guarantee the subordinate’s effort at least in the good-news days. Oppositely, the left-side zone (pink / yellow) is where no disclosure at all is optimal. This is where, once the subordinate realizes that it is a bad-news day, he would believe that very likely tomorrow and even later are bad, resulting in little effort from the subordinate for a long time. In order to avoid it, it is better to shut down the information completely from the beginning. The middle region (blue) is more complicated, where lying / jamming information is optimal. Fair or not, this way optimally controls the subordinate’s incentive.
The information and mechanism design problems in dynamic settings have been lively studied in recent years. You might think that analyzing the relationship of a leader and a subordinate in a firm is a “small” problem, but the theoretical tools and gained insights in these small problems are expected to be useful in analyzing “bigger” problems such as central bank’s communication policy with the market.
YAMASHITA, Takuro
Professor
Degree: PhD (Economics) (Stanford Univeristy)
yamashitat@osipp.osaka-u.ac.jp
































