Field of Research
International Economics, Trade Policy
Research Topics
International Trade, Development Economics, East Asian Economies
Overview of Research
A computable general equilibrium (CGE) model is an empirical tool well suited to evaluating policies that have regional and sectoral ramifications in the medium and long run. First, it captures extensive indirect effects, such as inter-industry linkages between sectors and trade linkages between countries. Second, it can evaluate the effects of removing trade barriers on resource allocation and structural adjustments over time. Third, it can detail the impacts on both member and nonmember countries in a free trade agreement (FTA), for example, and thereby better elucidate implications for the negotiating environment.
My current and future research topics using a dynamic CGE model are as follows:
1. I am currently evaluating the effects of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) on economic welfare, real GDP, and sectoral output and employment during 2020-2035 for Japan and other CPTPP member countries.
2. I am estimating the extent of losses to the US real GDP resulting from its withdrawal from the TPP, and the effects on sectoral output in the United States. In particular, which US sectors will be negatively affected is politically important.
Figure 1. Real GDP changes in the United States under alternative scenarios
(Absolute changes from the baseline, US$ billion in 2011 prices)
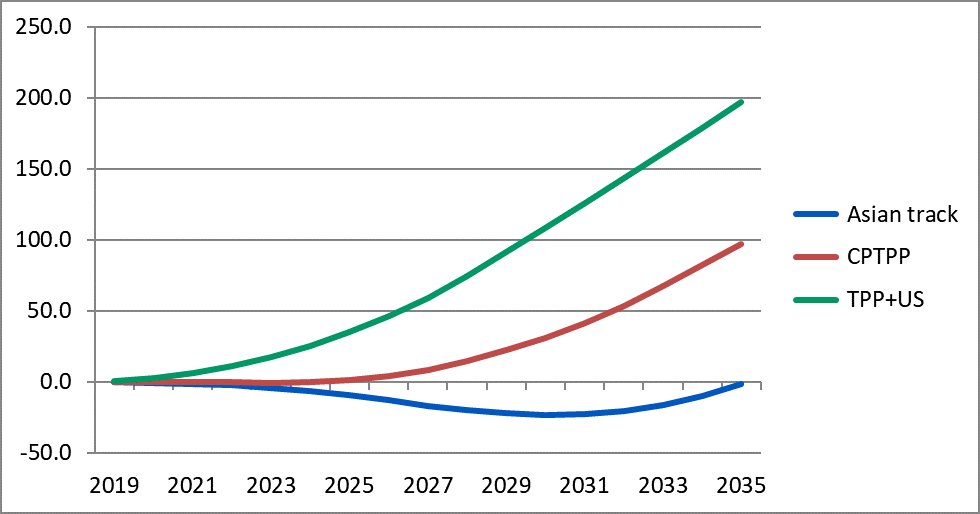
Figure 1 shows real GDP changes in the United States under three alternative scenarios. Under the Asian track scenario, it is assumed that the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is implemented over the period 2020-2029, and a Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP) comes into force in 2028, which 80% of implementation would be completed by 2035. Under the CPTPP scenario, TPP11 (CPTPP) is implemented during 2019-2028, TPP16 during 2024-2033, and 80% of FTAAP is implemented during 2028-2035. A hypothetical TPP+US scenario assumes that the US remained in the TPP, TPP12 is implemented during 2019-2028, TPP16 from 2024-2033, and FTAAP from 2028-2035. TPP+US is included mainly to compare the real GDP results of the United States under the first two scenarios with this hypothetical scenario.
3. My co-author and I have constructed a global CGE model that disaggregates imports of intermediate products by country of origin using the GTAP database and inter-country input-output tables. Using this modified model, we will examine the welfare and sectoral output effects of the CPTPP and RCEP. The preliminary results suggest that while incorporating the global value chains (GVC) structure does not significantly affect the overall welfare results, the magnitudes of changes in sectoral output become considerably greater in some industries.
4. When foreign direct investment (FDI) data by source country, host country and industry become available, we hope to endogenize FDI flows in our model.
Message to students
I regret to inform you that I will not be able to become a supervisor for students admitted to OSIPP after September 2019, since I will retire from Osaka University on August 31, 2019.
LEE, Hiro
Professor Lee has now retired his full faculty position.
Degree: Ph.D. in Economics (University of Calfornia, Berkeley)